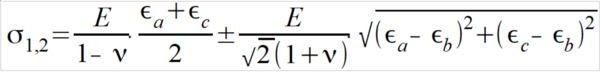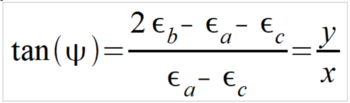Stress analysis with strain gauges
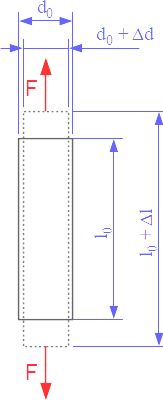
Stress analysis with strain gauges is used to determine the mechanical stress in a component.
In stress analysis with strain gauges, bridge circuits with only one active measuring grid are usually used.
In a uniaxial stress state, it is sufficient to measure the strain with a single measuring grid if the direction of the mechanical stress is known. The strain gauge is used to determine the amount of strain. To calculate the mechanical stress from the measured strain,
- the elastic modulus of the material and
- the k-factor of the strain gauge
must be known.
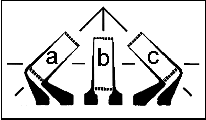
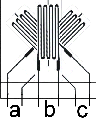
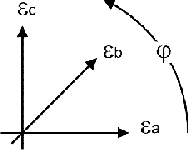
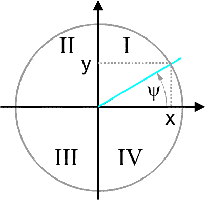
If the stress state is biaxial, the principal stresses and the direction of the principal stresses must be determined. Three determination equations are required to determine the three unknown quantities. Therefore, three measuring grids are used in three linearly independent directions, e.g. 0°, 45° and 90° or 0°, 60° and 120°.
For this task, strain gauge rosettes with three active measuring grids are available. To calculate the mechanical stress from the measured strain, the elastic modulus of the material, the Poisson's ratio of the material and the k-factor of the strain gauge must be known